Results
For the Estonian Health Insurance Fund, it is important to ensure continuous development of health services, so that the services meet the changing needs of healthcare professionals and individuals in terms of quality, usability, and cost-effectiveness.
The expected benefits of organizing a remote service pilot projects call were (1) finding remote service models with high potential; (2) establishing a practice for evaluating the impact of remote services; (3) developing reimbursement models for remote services.
In autumn 2023, four projects who received funding to carry out a pilot, submitted their impact assessment study results. The evaluation committee found that the results of three projects (Pre-visit, OTT, OnKontakt) were not sufficient to make an official proposal to add these new services permanently to the List of Health Care Services and make them available nationwide. Additional studies are needed to understand the full impact of the new service models.
The impact assessment results of the psoriasis remote monitoring project were sufficient to propose the new service be added to the List of Health Care Services. The official body met on January 17 2024, and decided that a follow-up study is needed in order to add the new service permanently to the list. Additional data needs to be gathered to assess the the effectiveness of the new service, and to conduct a cost-effectiveness analysis.
The aim of all new remote services is to be included in the permanent List of Health Care Services to obtain permanent funding. Although no new services were added to the list after the pilot project call, there were many learnings and results, which add value to the whole health care innovation in Estonia.
Interest and usage among the target groups
All four pilot projects showed that there is interest in such new services among patients and health care professionals alike. For example, in the OnKontakt project, 85 patients used the Kaiku Health platform. Patients and healthcare workers rated the platform's usability highly, with 77% of patients responding that the IT solution helped them independently manage issues related to their treatment. On average, one patient responded to questionnaires on the Kaiku platform 20.7 times over six months, or 3.5 times per month. Based on the responses to the questionnaires, the severity level was determined for a total of 22,436 treatment-related side effects.
At the end of the Pre-visit project, a quarter of patients considered MinuDoc their most frequent channel for contacting the primary care center, and contacting by phone decreased. Nurses began to play a bigger role. In 2022, patients contacted MinuDoc 32,071 times, including completing 10,441 symptom questionnaires for new health problems. This averages to one contact per patient per year and 0.37 times for completing symptom questionnaires.
In the OTT project, 168 patients used a new digital health plan to monitor their health. In total, 168 patients sent 755 messages over 13 months. Patients received a response from the primary care center team on average in 4 hours and 31 minutes. Thanks to the remote service, the customer experience of intervention group patients improved, and at the end of the study, 43% more patients in the intervention group achieved their target blood pressure values compared to the control group. 91% of intervention group patients rated the health plan as helpful in achieving their desired results by the end of the study period.
In the psoriasis remote monitoring project, both patients and healthcare workers rated the user-friendliness of the application used in the highly. Enough patients (77.15%) used the remote monitoring solution, allowing healthcare workers to make decisions about treatment or referral based on remote monitoring information. Usage activity was also sufficient to assess the feasibility and impact of this project's service model compared to conventional treatment. 87% of the patients involved expressed satisfaction with the new service, and 85% would recommend or strongly recommend the service to others. 68% of patients participating in the project expressed a desire to continue remote monitoring, with 70% still under monitoring even after the end of the sample project monitoring period. The study found that patients' readiness to use remote monitoring may be influenced by healthcare workers' active involvement in patients' treatment journey, ongoing support, and encouragement, as both the desire and need for such were highlighted in both patient focus groups and feedback, as well as usage activity analysis regarding the healthcare institution's workflow processes.
Route to permanent reimbursement
The route to permanent reimbursement is longer than initially assumed by the pilot projects call. Due to the rapid digitization, various countries have intensified the development of regulations in recent years to assess and fund digital health technologies on common grounds. Examples of this include Germany, Belgium, and the United Kingdom. The experience gained from the pilots serves as a basis for creating a similar framework and funding model in Estonia to increase transparency and provide clarity in the journey to obtaining permanent funding for new service models.
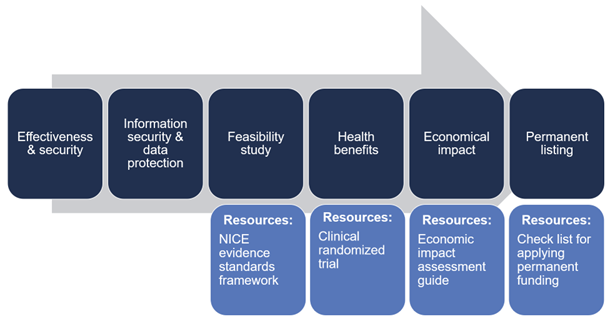
During the call, it became clear to the Health Insurance Fund that new service models containing digital solutions, first (1) the effectiveness and security of the digital solution should be evaluated; (2) then information security and data protection; (3) feasibility study should be carried out; (4) identify positive health benefits for individuals. For the Health Insurance Fund to make funding decisions, it is necessary to compare evidence-based data on the impact of the digital solution with current practice. The experience from sample projects showed that obtaining sufficient evidence requires more than just one study. The figure illustrates various stages. Further information can be found here.
Innovation grant
Creating new service models requires more than one-time open calls; it requires permanent funding and measures. The Health Insurance Fund's innovation grant is a permanent scheme that emerged from the experiences of pilot projects. Through innovation grant, it is possible to carry out impact assessment studies to obtain new evidence. The purpose of supporting impact studies is to obtain reliable information about the effectiveness and cost-efficiency of the implementation of services and the ease of use of services compared to the current best practice. More information can be found here.
Estonian Health Insurance innovation grant could be seen as a similar scheme to other countries initiatives – Germany’s DiGa, France’s PECAN or UK’s Early Value Assessment.
Impact assessment studies
Investigating the impact of new (digital) service models is still an evolving field. Internationally, there are no unified standards for researching healthcare technologies to measure the impact of a new solution most effectively. Digital solutions are products that are constantly evolving and highly dependent on end-users. For example, software can be continuously modified based on clinical performance and end-user input. Additionally, interventions can be continuously adjusted according to individual needs and changing circumstances. However, due to the flexibility of digital solutions, it is very difficult to measure their clinical impact and effectiveness.
In healthcare, the gold standard is a clinical randomized trial, but the structure of such a study may make it challenging for service models containing digital solutions to demonstrate their full value. It is important for the Health Insurance Fund to ensure that individuals receive the best possible treatment, considering the evidence-based nature of the treatment, medical effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness. Until there are specific agreements and good examples of conducting studies on digital solutions, we rely on the best practices of randomized clinical trials for research on digital solutions as well.
In designing the impact studies of pilot projects, the NHS’s NICE framework was used as a guiding material. The experience with the NICE framework showed that the framework is a useful tool for conducting initial feasibility studies, but to obtain permanent funding, one study alone is not sufficient. More research is needed to obtain stronger evidence.
The figure illustrates various stages. More information can be found here.
New reimbursement models
New service models also require new ways of reimbursing. Financing for Estonian healthcare services is largely based on the fee-for-service model. This approach does not support integrated patient care.
Integrated payment models were tested within the framework of pilot projects. The reimbursement model tied together the technological component and the healthcare worker's time. In addition, the call also experimented with outcome-based performance pay related to patient health and experience indicators. This meant that payment was based on the final outcome and impact on the patient, rather than the number of procedures performed.
These are important experiments because when using such payment models, healthcare service providers engage in closer collaboration and are motivated to make organizational changes, including in quality systems for e-services and training, to ensure that patients receive assistance in the best possible way.
Funding clinical assistants and treatment planning through the List of Health Care Services
The payment models tested in pilots included compensation for new roles and activities of healthcare workers. Some of which have been partially included in the permanent Health Care Services List, meaning they are funded for all healthcare service providers.
An important part of the Pre-visit project was the clinical assistant/health analyst, who supported the work of primary care centers in managing and resolving patient concerns. Since July 1, 2023, compensation for primary care clinical assistants has been included in the List of Health Care Services, allowing additional workforce to be brought to primary care to provide medical care under increasing workload. This allows the family doctor to focus on medical work while the team around them supports them in administrative activities.
One part of the service in the proactive health journey digital designer project (OTT) was the creating a treatment plan for the patient. The health center, in collaboration with the patient, created a personalized health or treatment plan using motivational interviewing, which included the patient's goals and activities. The role of the family doctor and their team was to empower patients to take care of their health. Funding for treatment planning is also provided through the healthcare services list as of July 1, 2023.
Primary care digital service channels
Primary care digital service channels project emerged from the pilot project competition. Its aim is to support general practitioners in the implementation of digital service platforms, allowing all Estonian residents to access primary care centers through digital service platforms. The Health Insurance Fund sets specific requirements for digital service platforms, assesses compliance with these requirements, and reimburses compliant platforms through the healthcare services list. General practitioners can choose the most suitable digital platforms from among those that meet the requirements. The auditing process is similar to NHS’s Digital Technology Assessment Criteria evaluation.
Cooperation
Successful innovation in healthcare can only occur through open collaboration with other stakeholders in the health system. Health insurance institutions have traditionally been distant from innovation and entrepreneurship, and the Health Insurance Fund has taken on a new role with the organization of such a call. The pilots call brought together various stakeholders under the leadership of the Health Insurance Fund from the outset – healthcare service providers, academia, entrepreneurship, health insurance, and policymakers. Better-integrated healthcare services are essential in the future, and it is important, as new roles emerge and are assumed, to transparently and clearly communicate where investments are being made and what roles are being taken on.
Final report of the process analysis for the telemedicine pilot project
The purpose of the analysis is to describe and analyse the innovation contest organised by the Health Insurance Fund and the related activities, and to assess the effectiveness of the competition in meeting the objectives of developing remote healthcare services. This report summarises the main findings and recommendations of the interim reports and is also available in Estonian. Find the report here.